Figure 1. Structure of HSV-1 (A Handbook of Gene and Cell Therapy)
Herpes simplex virus (HSV) is a large, enveloped, double-stranded DNA virus with a genome size ranging from 150 kb to 240 kb, encoding approximately 90 viral proteins. It has an average diameter of 180 nm, including a 125 nm icosahedral capsid. Commonly used HSV vectors are divided into replicating oncolytic vectors and replication-defective vectors.
Oncolytic HSVs (oHSVs) are genetically engineered to selectively replicate within tumor tissue, thereby infecting and killing tumor cells. HSV has advantages such as a broad host range, high infection efficiency, short replication cycle, large genome capacity, and weak pathogenicity. Additionally, antiviral drugs such as acyclovir or ganciclovir effectively inhibit viral replication. Therefore, HSV-1 has been widely studied and applied as an oncolytic viral product in recent years.
Figure 2. Genome structure of HSV-1
The HSV genome consists of two unique regions (unique long [UL] and unique short [US]), each flanked by a pair of inverted repeats, TRL/IRL and IRS/TRS. An "a" sequence is located at the junction between IRL and IRS, situated between the UL and US sequences.
Genevoyager possesses expertise in the recombination, rescue, and expansion of oHSVs. We can design the optimal path and efficiently construct oHSVs mutants and recombinant strains based on client needs. For example, we can knock out specific genes in commonly used oHSV-1 viruses, such as ICP34.5 (RL1), ICP47, US11, and TK, to achieve tumor selectivity. On the other hand, we can insert exogenous genes, such as GM-CSF and IL12, at specific sites to enhance immune responses. To further improve tumor targeting and safety, we can modify HSV-1 according to client requirements. We have a variety of HSV-1 strains, including KOS, F, and H129.
|
Name |
Strain |
Modification |
|
T-Vec |
JS1 |
Double deletion of ICP34.5, insertion of GM-CSF at this site; deletion of ICP47. |
|
G47Δ |
F |
Double deletion of ICP34.5; deletion of ICP47; disruption of ICP6 reading frame and insertion of LACZ. |
|
NV1020 |
R7020 |
Single deletion of ICP0, ICP4, ICP34.5, deletion of UL56, replacement of TK with HSV-2 TK. |
|
rQNestin 34.5 |
F |
Insertion of nestin promoter before ICP34.5. |
|
M032 |
F |
Double deletion of ICP34.5, expression of IL-12 at this site. |
|
ONCR-177 |
ONCR-159 |
Single deletion of ICP34.5, introduction of tissue-specific miRNA to regulate ICP34.5 expression; UL37 mutation; insertion of IL12, FLT3LG, CCL4, PD-1 antagonist, and CTLA-4. |
|
C134 |
Chimeric oHSV |
Single deletion of ICP34.5, insertion of IRS1 between UL3 and UL4. |
|
RP1/2 |
Clinical strain |
Double deletion of ICP34.5, insertion of GM-CSF and GALV-GP-R at this site; deletion of ICP47. |
|
Rrp450 |
Genetically engineered HSV |
Deletion of ICP6 and insertion of CYP2B1. |
|
OH2 |
HSV-2 |
Double deletion of ICP34.5, insertion of GM-CSF at this site; deletion of ICP47. |
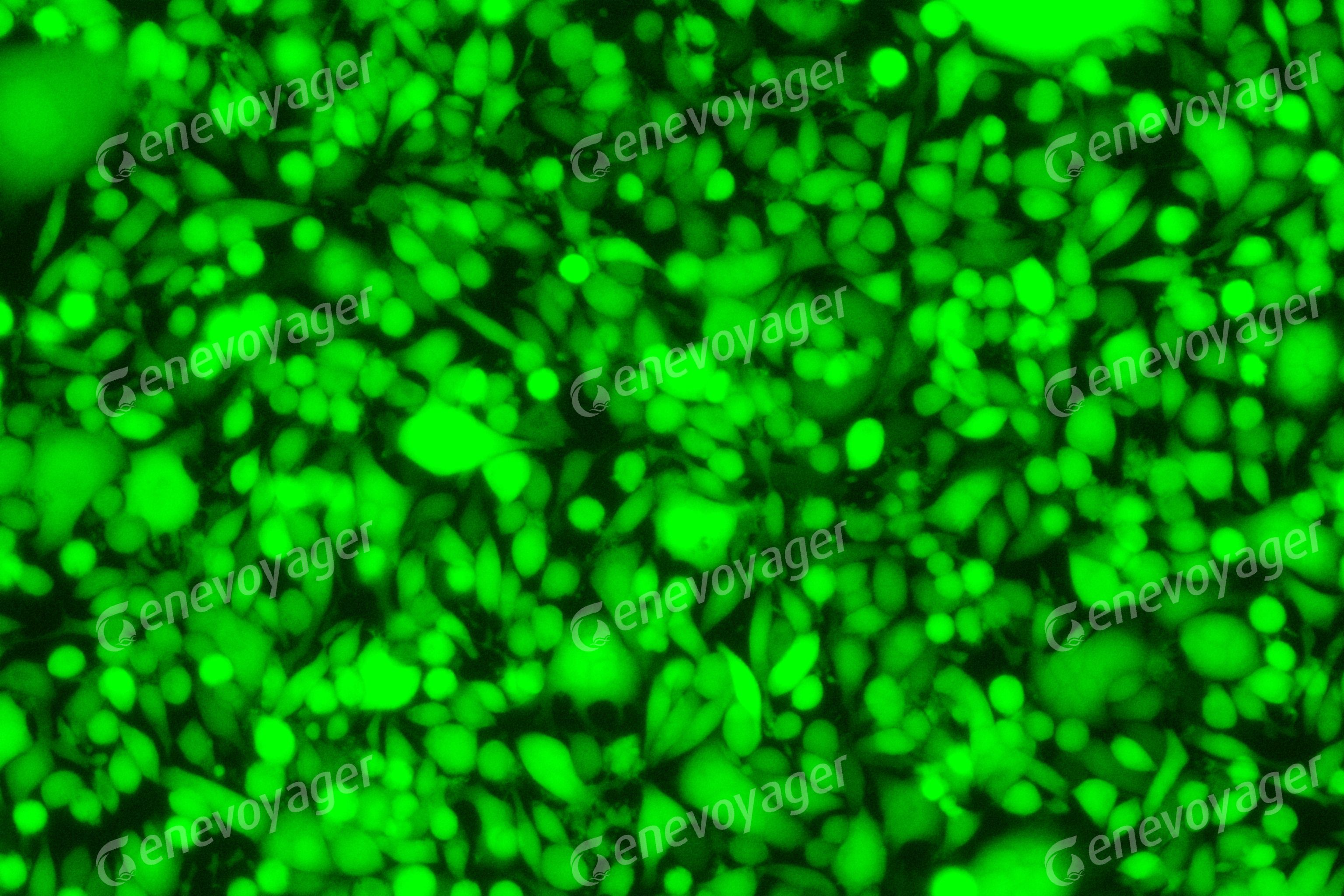
Figure 4. BHK21 cells infected with HSV viral particles (product number: H06001)
produced by Genevoyager after 24 hours


US: 3675 Market Street, Suite 200, Philadelphia, PA19104 Tel: +1 (215) 205-6963 | +086 027-65023363
E-mail: hui.wang@genevoyager.com / vector@genevoyager.com
China: No128, Guanggu 7th Rd, East Lake High-tech Development Zone, Wuhan, China Tel: 17720522078
E-mail: marketing@genevoyager.com